Cerebral and Spinal DSA
HomeCerebral and Spinal DSA
Cerebral and Spinal DSA
What is a diagnostic cerebral angiogram (DSA):
A Diagnostic cerebral angiogram (DSA) is a test performed to study the blood vessels which supply the brain. It involves angiographic studies of the blood vessels in the neck and inside the skull. The entire study details the study of the carotid arteries ( external and internal carotid arteries) in the neck on the left and right side, the internal carotid arteries on both sides inside the skull and the 2 vertebral arteries in the back of the neck and the brain (the vertebro-basilar system).
Pre- procedure: The person has to be fasting prior to the procedure. Basic blood tests are performed prior to the procedure. Patients with allergies, kidney disease, diabetes, bleeding problems or on blood thinners, pregnant and lactating mothers need to inform the doctor of their medical condition prior to the angiogram.
Digital subtraction angiogram and right sided stroke in a patient with Moyamoya disease
Procedure: The procedure is performed in a cath lab. Most diagnostic angiograms are performed under sedation. The arterial system is entered through the femoral artery through the right groin and using this portal of entry a diagnostic catheter is threaded over a guide wire to each of the individual vessels mentioned above. This is done using a special cath lab machine ( which is an advanced Xray Machine) calibrated to study the blood vessels. A radio-opaque dye in injected through the previously positioned catheter and the cath lab machine subtracts bone structures to provide a view of the blood flow in the blood vessels of the brain- the arteries- capillary phase and then into the veins and away from the brain. During the study details on various disorders of the cerebral vasculature is provided. Using special computer software a 3-D picture of the blood vessels of the brain can be derived.
After procedure: The puncture site is sealed with either manual compression or with a special closure device. The person needs to lie flat in bed without moving the leg on the site of puncture for a specified period of time. If the procedure is performed well in time , the person can go home the same evening
What are the risks: It is an invasive procedure and is not without risks. The risks include bleed at the puncture site, reaction to the dye injected. The risk of suffering a stroke after an angiogram is less than 1%. However, the risk of having a permanent
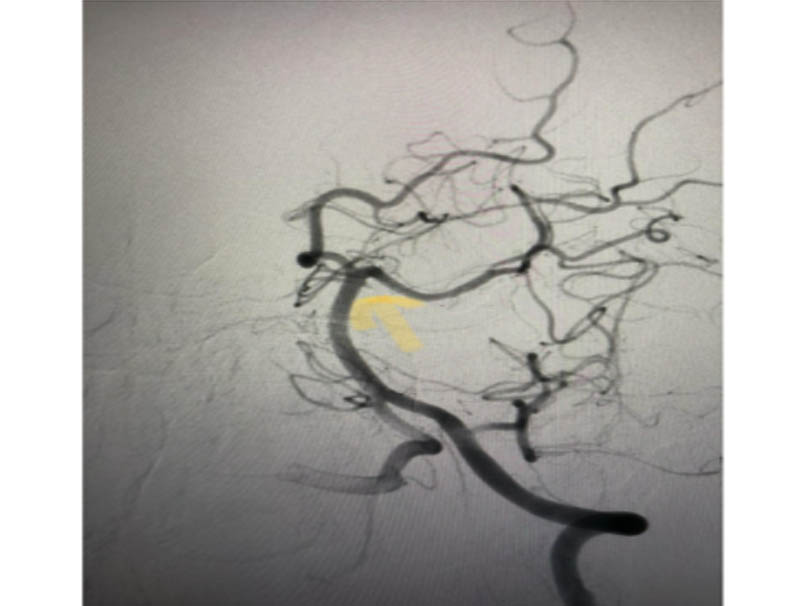
Image of a angiogram of the vertebrobasilar system
