Usage of Sunscreen in Children
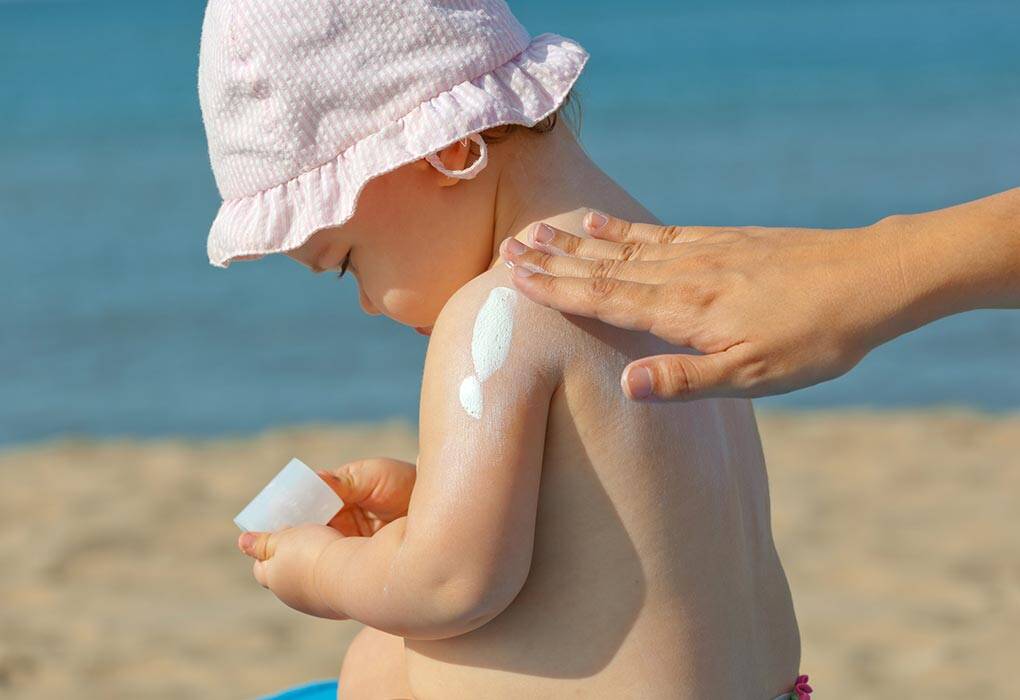

What’s the best way to protect my children from the sun?
Sunscreen needs to applied -don’t save your sunscreen for sunny days only – Upto 80 percent of the sun’s ultraviolet rays can pass through the clouds. Follow these sun safety tips daily:
Apply the right amount of sunscreen – with a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 30 – to cover all the exposed areas of the body. To give you an idea of how much sunscreen you’ll need – It take a tablespoon to cover the exposed areas of the body of an adult – a little less for a child depending on his or her size. Make “More Is Better” your motto!
Apply sunscreen 20 to 30 minutes before heading outdoors as it can take 30 minutes for a sunscreen to start working. The ingredients in the sunscreen kick start being active in half hour.
Reapply sunscreen every two hours and after a dip in the pool, even if you are using a water-resistant product. Sunscreens rub, wash and sweat off easily. If your child is playing sports and sweating a lot, reapply more frequently.
Wear protective clothing, a broad-brimmed hat, lip balm with an SPF and sunglasses. Clothing with a tight weave provides the best protection – hold your favourite shirt up to the sun so see how much light comes through. For example, a dry, white T-shirt typically only offers an SPF of about 7.
Stay in the shade during the sun’s peak hours of 10 a.m. to 4 p.m.
Remember, too, that the sun reflects from sand, water and the pavement, so make sure your kids apply sunscreen all over to protect themselves from the sun’s rays whether they come from above or below.
Broad-spectrum is best. Choose a sunscreen that provides broad-spectrum (this will be listed on the packaging) coverage against both ultraviolet A (UVA) and ultraviolet B (UVB) light. These are the rays of the sun that can cause sunburn, skin damage, cancer and wrinkles.
Go for at least SPF 30. Pick a product that is water-resistant and has a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 30. Anything above 30 does not give you that much additional protection. The SPF number on the sunscreen bottle is a guide to how long you can stay in the sun without risking sunburn. This is calculated by comparing the amount of time it takes to get sunburn on sunscreen-protected skin, compared to the time it takes to cause sunburn on unprotected skin. For example, it takes about 10 minutes for unprotected skin to burn; whereas with an SPF 15 sunscreen, it takes 150 minutes to burn. Currently, SPF refers only to protection from UVB light.
Zinc oxide or titanium dioxide for young children and those with sensitive skin. Look for these ingredients if you have infants or young children , or you or your kids have sensitive skin or eczema. These ingredients physically block the sun’s rays from penetrating the skin. Chemically-based products absorb the sun’s rays and dissipate them as heat. These are also effective and safe for older children and adults without any skin sensitivities.
A lack of this important vitamin can cause serious illnesses such as rickets, a disease that weakens bones. Sun exposure is one way of obtaining vitamin D and wearing sunscreen does decrease the skin’s production of it. However, intentional sun exposure is not the best option for your child’s health. Instead talk to your doctor about adding more vitamin D rich foods to your children’s diet or taking a daily supplement.